
Chemiluminescent substrate for Western Blot
Chemiluminescent substrates have revolutionized protein detection in Western blotting, a widely used technique in molecular biology and biochemistry for analyzing specific proteins within complex mixtures. These substrates enable highly sensitive and specific detection by producing light in a reaction catalyzed by enzyme-linked antibodies, allowing researchers to visualize and quantify proteins of interest with remarkable precision. This introduction delves into the principles, applications, and advancements of chemiluminescent substrates in Western blotting, highlighting their critical role in modern science.
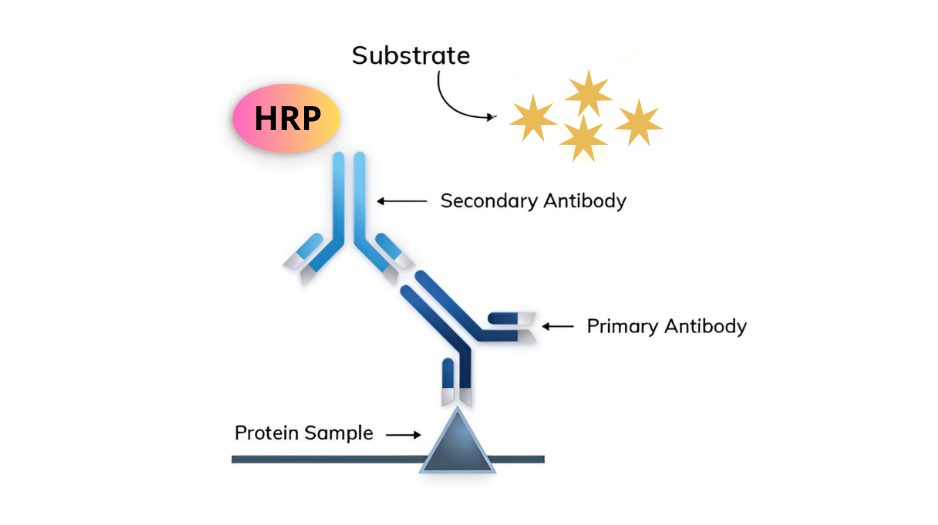
Figure 1. Chemiluminescent Western blotting- one signal, one protein.
Key Features of Chemiluminescent Substrates
-
High Sensitivity: The enzymatic reaction catalyzed by horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or alkaline phosphatase (AP) amplifies the signal, enabling detection of femtogram quantities of proteins. This sensitivity is ideal for studying low-abundance proteins.
-
Specificity: The multi-step antibody binding ensures precise targeting of the protein of interest, making it suitable for detecting post-translational modifications or closely related proteins.
-
Long-Lasting Signals: Modern substrates produce brighter and longer-lasting luminescent signals, enhancing reproducibility and reducing signal capture time.
Advancements in Chemiluminescent Substrates
-
Enhanced Chemiluminescent (ECL) Substrates:
-
Products like NeoPRO ECL substrates and NeoPRO RTU offer superior performance by increasing the signal intensity and duration.
-
These advancements expand the dynamic range of detection, facilitating more accurate protein quantification.
-
-
Multiplexing Capabilities:
-
Chemiluminescence enables simultaneous analysis of multiple proteins, aiding studies of complex signaling pathways and protein interactions.
-
-
Compatibility with Digital Imaging:
-
Imaging systems with CCD or CMOS sensors provide higher sensitivity and resolution than traditional X-ray films, streamlining data analysis and improving reproducibility.
-
Applications in Research and Diagnostics
-
Biomedical Research:
-
Oncology: Detecting oncogenes and tumor suppressors to explore cancer mechanisms.
-
Neuroscience: Analyzing synaptic proteins to understand neurodegenerative diseases.
-
Immunology: Quantifying cytokines and antibodies for immune response studies.
-
-
Clinical Diagnostics:
-
Identifying biomarkers for infectious diseases.
-
Detecting autoantibodies in autoimmune diseases for accurate diagnosis.
-
-
Drug Development:
-
Monitoring therapeutic targets and evaluating drug efficacy.
-
Advantages Over Other Methods
-
Cost-Effectiveness:
-
Requires basic laboratory equipment, making it accessible for labs with limited budgets.
-
-
Versatility:
-
Suitable for analyzing proteins in various samples, including cell lysates, tissue homogenates, and purified preparations.
-
-
Ease of Use:
-
Simplified workflows and readily available substrates ensure user-friendly protocols.
-
Resultado da sua pesquisa : 2 produto encontrado
Refine sua procura :
- Buffers and reagents 2
- WB

